Solar energy is gaining popularity worldwide, including in India, where both homeowners and businesses are increasingly considering it as a viable option to reduce electricity bills and carbon footprint. There are two main types of solar systems: on-grid (grid-tied) and off-grid (standalone). Understanding their differences can help you decide which is best for your needs.
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied system, is connected to the local utility grid. Here is how it works:
Advantages of On-Grid Solar Systems:
Disadvantages of On-Grid Solar Systems:
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar system operates independently from the local utility grid. Here is how it works:
Advantages of Off-Grid Solar System:
Disadvantages of Off-Grid Solar System:
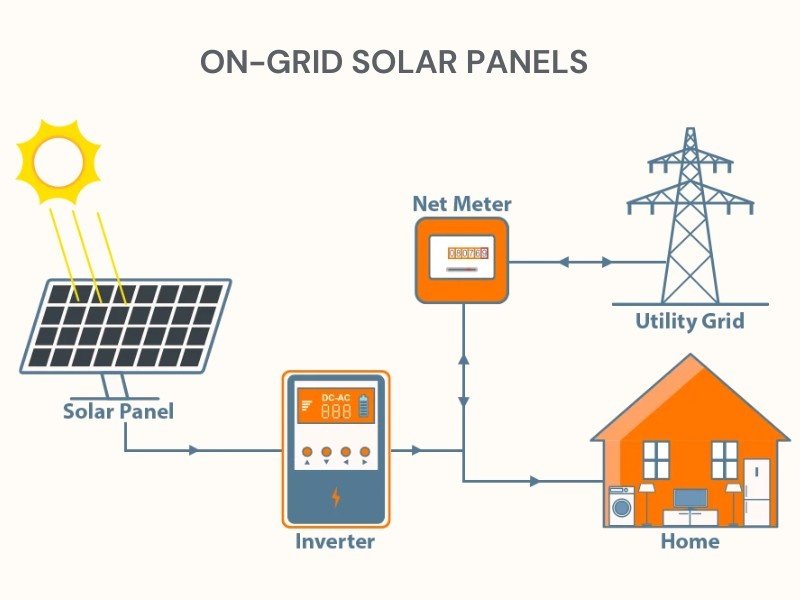
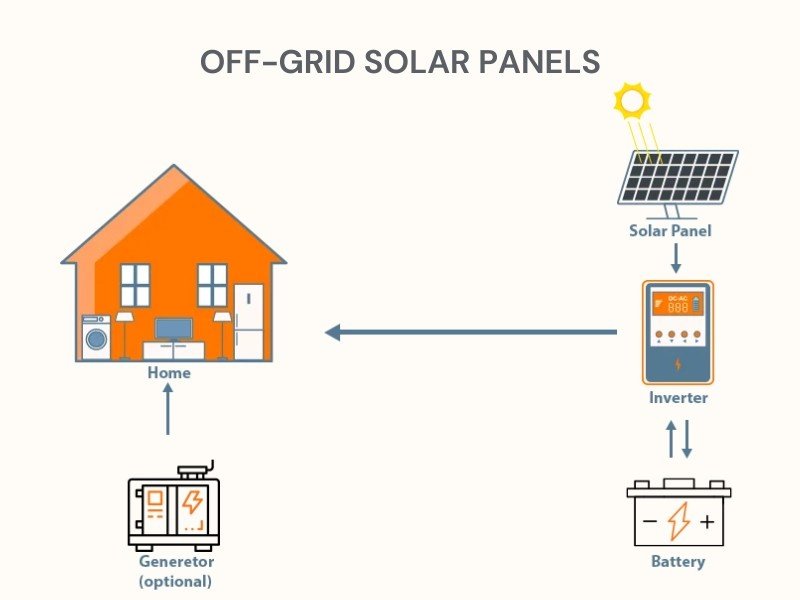
Key Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems
An off-grid solar system operates independently from the local utility grid. Here is how it works:
1. Access to Electricity:
2. Cost:
3. Power Outages:
4. Energy Independence:
What Are Hybrid Solar Systems?
Hybrid solar systems combine the benefits of both on-grid and off-grid systems:




