Welcome To Alpex
On-Grid Solar Panels for Home-Working, Subsidy, ROI and Price
Transform your home with Alpex’s cutting-edge solar modules. Experience energy independence and substantial savings on your electricity bills.
Panel Installations
Experienced Engineers
Years of Experience
Customer Satisfaction
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
How Does On-Grid System Work?
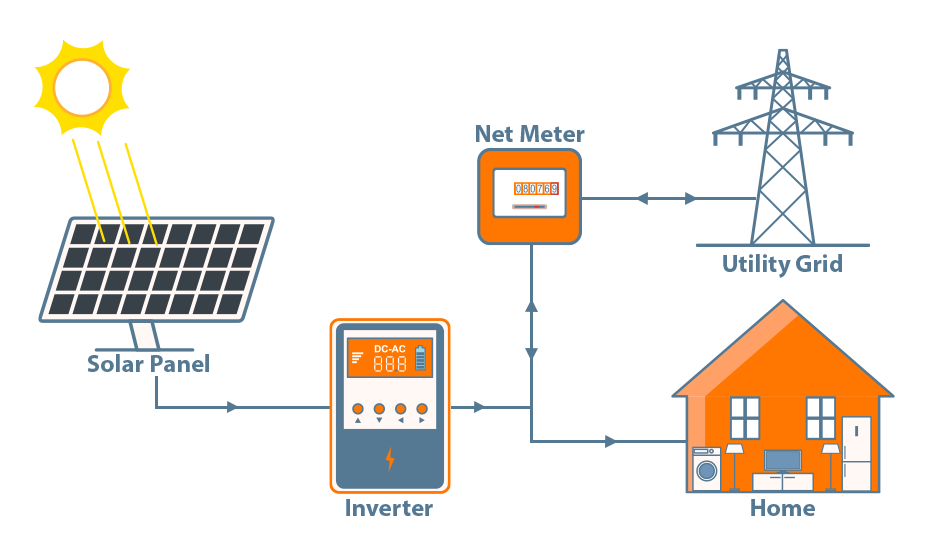
Here is how on grid system works-
- Solar Panels absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic (PV) process.
- The DC electricity generated by the panels is sent to an inverter. The inverter converts this DC into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in homes and businesses.
- Once converted to AC, the electricity is used to power appliances. When the system generates more electricity than needed, the excess is sent to the public electricity grid.
- Any extra electricity generated that is not used immediately is exported back to the grid. Depending on your location, you may receive credits or payments for this surplus energy through a process called net metering.
- At night or on cloudy days when the system isn’t generating enough solar power, electricity is automatically drawn from the grid to meet your needs, ensuring an uninterrupted supply of power.
Key Components of an On-Grid Solar System
To understand how an on-grid solar system functions, it is essential to know about its key components:
1. Solar Panels:
The solar panels are the heart of any solar energy system. These panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells that trap sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The efficiency of the solar panels determines how much energy you can generate, which is why choosing high quality panels is crucial.
2. Inverter:
The electricity generated by the solar panels is in DC form, but your home appliances use alternating current (AC). This is where the inverter comes in. It converts the DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity. Inverters are a critical component so their efficiency impacts the overall performance.
3. Grid Connection::
The connection to the local utility grid is what makes on-grid systems unique. This connection allows you to draw power from the grid when needed and send excess energy back. A bidirectional metre is used to track the energy you consume from the grid and the energy you export, facilitating the net metering process.
Comparing On-grid vs Off Grid:
Off-grid systems operate independently from the utility grid, relying on battery storage for power when the sun isn’t shining. While they provide energy independence, they require a higher investment in batteries and maintenance. Conversely, on-grid systems are more cost-effective and efficient, especially in urban or suburban areas with reliable grid connectivity. On-grid systems have lower initial costs and do not need expensive batteries, making them a practical choice compared to the higher costs and maintenance of off-grid and hybrid systems.
Factors to consider before installing an on-grid solar system
The solar panels are the heart of any solar energy system. These panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells that trap sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The efficiency of the solar panels determines how much energy you can generate, which is why choosing high quality panels is crucial.
- Site Assessment: A professional site assessment will determine whether your home receives enough sunlight and has adequate roof space for solar panels. Factors like shading, roof orientation, and local climate play a significant role in the system’s efficiency.
- Sizing Your System: The size of your solar system should match your energy consumption needs. This involves calculating your average daily energy use and ensuring that the system you install can meet these demands.
- Connecting to the Grid: The installation process includes securing permits, installing the solar panels and inverter, and connecting the system to the grid. Working with a certified installer ensures that the process is smooth and that your system is up to code.
Financial Incentives and Government Support
To encourage the adoption and usage of solar energy, many governments offer financial incentives:
- Solar Subsidies: Many regions offer subsidies, discounts, or tax benefits for solar installations, which can significantly lower the initial cost of your system. These incentives vary by location, so it is essential to research for what is available in your area.
- Electricity Buyback and Net Metering: These programs let you sell any extra electricity your solar panels generate back to the grid. This means you can earn money for the surplus energy, helping you recover the cost of your solar system faster and boost your savings.
Advantages of On Grid Solar Systems
On grid solar systems offer several benefits that make them an attractive option for homeowners and businesses looking to reduce their energy costs and environmental impact.
1. Cost Savings:
By generating your power, you decrease your reliance on the utility company, which translates into lower monthly energy costs. Over time, the savings can offset the initial investment in the solar system, making it a financially good choice.
2. Net Metering:
Many regions offer net metering programs, which allow homeowners with on-grid solar systems to earn credits for the excess electricity they send back to the grid. These credits can then be used to offset the cost of electricity you consume from the grid, further reducing your overall energy costs.
3. Low Maintenance:
On-grid solar systems are relatively low maintenance compared to other types of renewable energy systems. Since there are no batteries involved, the system's complexity is reduced, and the components generally require minimal care. Regular cleaning of the solar panels and periodic inspections are usually sufficient to keep the system running efficiently for many years.
Impact of Power Outages on On-Grid Solar Systems
One of the key considerations for on-grid solar systems is their reliance on the grid for smooth operation. In India, where power outages can be frequent, it is important to understand how they affect on-grid systems. When the grid goes down, on-grid solar systems automatically shut off as a safety measure to prevent electricity from being fed back into the grid, which could endanger utility workers repairing the lines. This means that during a blackout, even though your solar panels may still be generating electricity, it won't be usable unless you have battery storage or a backup system.
However, adding a battery backup or exploring hybrid solar options can provide a solution, allowing you to store excess energy and access it during outages. While on-grid systems are cost-effective and efficient for daily use, it is important to evaluate your local electricity reliability and consider whether an additional investment in storage might be worth the long-term benefits for energy security.
Featured Products
Our product range includes:



